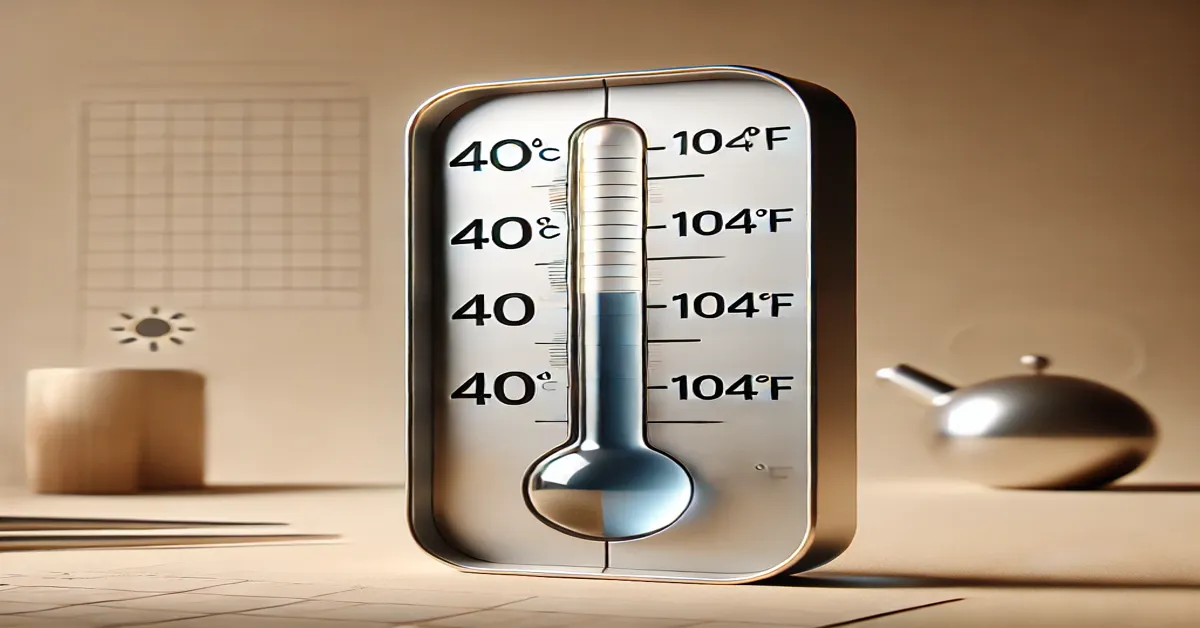
Converting temperatures between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a fundamental skill useful in everyday life, scientific research, cooking, and global communication. For example, if you’re planning a trip, cooking a dish that requires precise heat settings, or interpreting weather data, knowing how to convert 40 Celsius to Fahrenheit ensures you make informed decisions. This article delves into the significance of temperature conversions, the mathematics behind them, and the practical implications of understanding these temperature scales.
The Basics of Celsius and Fahrenheit
The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is a temperature measurement system used globally, especially in scientific contexts. In this scale:
- 0°C represents the freezing point of water.
- 100°C marks its boiling point under standard atmospheric conditions.
The Fahrenheit scale, in contrast, is predominantly used in the United States and a few other countries. Its defining points are:
- 32°F as the freezing point of water.
- 212°F as its boiling point.
The difference between the two scales lies in the intervals they use to define the freezing and boiling points of water, which is why converting 40 Celsius to Fahrenheit requires a specific formula.
The Formula for Conversion
To convert a temperature from 40 Celsius to Fahrenheit, the formula is:
Each degree Celsius equals 1.8 degrees Fahrenheit. Adding 32 adjusts for the difference in the freezing points of water on the two scales. Let’s apply this formula to convert 40 Celsius to Fahrenheit:
- Multiply 40 by 9/5 (or 1.8): 40 × 1.8 = 72
- Add 32: 72 + 32 = 104
Thus, 40 Celsius equals 104 Fahrenheit (40 Celsius to Fahrenheit)
Why Is 40 Celsius Significant?
A temperature of 40°C (104°F) is significant for several reasons:
1. Human Health
High temperatures, such as 40°C, can lead to heat-related illnesses, including:
- Heat Exhaustion: Symptoms include heavy sweating, rapid pulse, and dizziness.
- Heat Stroke: A medical emergency marked by confusion, nausea, and potential organ failure.
Understanding that 40 Celsius equals 104 Fahrenheit is crucial when assessing safety measures during heatwaves.
2. Environmental Impact
In many regions, 40°C signals extreme weather conditions. Prolonged exposure to such heat can:
- Stress ecosystems.
- Increase the risk of wildfires.
- Exacerbate drought conditions.
3. Infrastructure Challenges
At 40 Celsius (104 Fahrenheit), infrastructure systems, such as roads and railways, may face disruptions. Energy demand surges due to increased use of air conditioning, potentially leading to blackouts.
Practical Applications of the Conversion
1. Weather Interpretation
Travelers often encounter temperature scales unfamiliar to their home country. Knowing that 40 Celsius equals 104 Fahrenheit helps interpret weather forecasts effectively, ensuring preparedness for high temperatures.
2. Cooking and Baking
Recipes from different countries list oven temperatures in either Celsius or Fahrenheit. Accurately converting 40 Celsius to Fahrenheit ensures dishes are cooked to perfection, avoiding undercooked or overcooked results.
3. Science and Engineering
In scientific research and international engineering projects, temperature conversions maintain consistency in data interpretation and collaboration.
Historical Context of Temperature Scales
1. Celsius Scale
Developed by Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius in 1742, the original scale was reversed, with 0 as the boiling point and 100 as the freezing point. The current format was later adopted for its logical progression.
2. Fahrenheit Scale
Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit introduced his scale in 1724. Its zero point was based on the coldest temperature he could achieve using a mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride. The scale’s 100-degree point approximated human body temperature.
Global Usage of Temperature Scales
While Celsius is the international standard, Fahrenheit remains prevalent in the United States. This disparity often necessitates conversions like 40 Celsius to Fahrenheit, especially in global contexts.
Quick Approximation Techniques
For mental calculations, approximate conversions can be handy:
- Celsius to Fahrenheit: Double the Celsius temperature and add 30.
- Fahrenheit to Celsius: Subtract 30 from the Fahrenheit temperature and halve the result.
Using the approximation method:
- 40 Celsius: (40 × 2) + 30 = 110 (actual: 104 Fahrenheit).
Though slightly off, these shortcuts are useful for quick estimates.
Tools for Temperature Conversion
With technological advancements, converting temperatures like 40 Celsius to Fahrenheit is easier than ever:
1. Smartphone Apps
Many free apps provide instant temperature conversions. Inputting 40 Celsius will quickly display its Fahrenheit equivalent.
2. Online Calculators
Web-based tools allow for accurate conversions with a simple input and click.
3. Virtual Assistants
Devices like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant can convert temperatures on command.
Conclusion
Understanding temperature conversions, such as 40 Celsius to Fahrenheit, is an essential skill in various aspects of life. Whether you’re cooking, traveling, or analyzing scientific data, being able to switch between these two scales enhances comprehension and decision-making. By mastering the formula, historical context, and practical applications of these temperature scales, you’re better equipped to navigate a globally interconnected world.
FAQs
1. What is 40 Celsius in Fahrenheit? 40 Celsius equals 104 Fahrenheit.
2. Why do we need to convert temperatures? Temperature conversions are crucial for accurate weather interpretation, scientific research, cooking, and travel.
3. How do I convert Celsius to Fahrenheit? Use the formula: °F = (9/5) °C+32
4. Is 40 Celsius a high temperature? Yes, 40 Celsius (104 Fahrenheit) is considered very high and can pose health and environmental risks.
5. Are there tools for converting temperatures? Yes, smartphone apps, online calculators, and virtual assistants can convert temperatures instantly.
6. What is the difference between Celsius and Fahrenheit? Celsius is based on water’s freezing (0°C) and boiling points (100°C), while Fahrenheit uses 32°F and 212°F, respectively.